20200115-005a: Common Variance Requests Conditions Table — original pdf
Backup
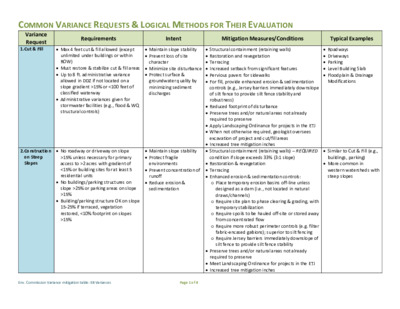
COMMON VARIANCE REQUESTS & LOGICAL METHODS FOR THEIR EVALUATION Requirements Intent Mitigation Measures/Conditions Typical Examples Variance Request 1. Cut & Fill • Max 4 feet cut & fill allowed (except unlimited under buildings or within ROW) • Must restore & stabilize cut & fill areas • Up to 8 ft. administrative variance allowed in DDZ if not located on a slope gradient >15% or <100 feet of classified waterway • Administrative variances given for stormwater facilities (e.g., flood & WQ structural controls) • Maintain slope stability • Prevent loss of site character • Minimize site disturbance • Protect surface & groundwater quality by minimizing sediment discharges • Structural containment (retaining walls) • Restoration and revegetation • Terracing • Increased setback from significant features • Pervious pavers for sidewalks • For fill, provide enhanced erosion & sedimentation • Roadways • Driveways • Parking • Level Building Slab • Floodplain & Drainage Modifications 2. Construction on Steep Slopes • Maintain slope stability • Protect fragile environments • Prevent concentration of runoff • Reduce erosion & sedimentation • No roadway or driveway on slope >15% unless necessary for primary access to >2 acres with gradient of <15% or building sites for at least 5 residential units • No buildings/parking structures on slope >25% or parking areas on slope >15% • Building/parking structure OK on slope 15-25% if terraced, vegetation restored, <10% footprint on slopes >15% controls (e.g., Jersey barriers immediately downslope of silt fence to provide silt fence stability and robustness) • Reduced footprint of disturbance • Preserve trees and/or natural areas not already required to preserve • Apply Landscaping Ordinance for projects in the ETJ • When not otherwise required, geologist oversees excavation of project and cut/fill areas • Increased tree mitigation inches • Structural containment (retaining walls) – REQUIRED condition if slope exceeds 33% (3:1 slope) • Restoration & revegetation • Terracing • Enhanced erosion & sedimentation controls: o Place temporary erosion basins off-line unless designed as a dam (i.e., not located in natural draws/channels) o Require site plan to phase clearing & grading, with o Require spoils to be hauled off-site or stored away temporary stabilization from concentrated flow o Require more robust perimeter controls (e.g. filter fabric-encased gabions); superior to silt fencing o Require Jersey barriers immediately downslope of silt fence to provide silt fence stability • Preserve trees and/or natural areas not already required to preserve • Meet Landscaping Ordinance for projects in the ETJ • Increased tree mitigation inches • Similar to Cut & Fill (e.g., buildings, parking) • More common in western watersheds with steep slopes Env. Commission Variance mitigation table: EB Variances Page 1 of 4 Variance Request 3. Stream Buffers (CWQZ & WQTZ) 4. Critical Environment al Features (CEFs) and CEF Buffers COMMON VARIANCE REQUESTS & LOGICAL METHODS FOR THEIR EVALUATION Requirements Intent Mitigation Measures/Conditions Typical Examples • CWQZ: dev't prohibited (except fences, • Keep development out of • Additional public open space area designation (or • CWQZ variances parks, trails, docks, etc.). Utility lines may cross CWQZ (Director approval needed in BSZ). Street crossings in CWQZ limited (except Urban wsheds). Limits vary with wshed (e.g., BSZ, WS Rural) & waterway classification (major, intermed., minor). No variances to CWQZ in BSZ (SOS). • WQTZ: 30% IC allowed in Suburban & 18% in WS Sub. wsheds: few variances requested. In BSZ & WS Rural wsheds, WQTZ same as CWQZ (except SFR OK if min. lot size 2 ac. & max. density 1 unit/3 ac.); WQTZ variances possible in BSZ (is not SOS). • CEFs include: bluffs, canyon rimrocks, caves, sinkholes, springs, & wetlands • Caves and sinkholes protected by 150- 300 ft. buffer; must be protected from runoff through drainage patterns and/or special controls. • SFR lots may not include or be within 50 ft. of CEF • Administrative variances are allowed if all characteristics of the CEF and related water quality/quantity functions are preserved. • Preservation/setbacks/mitigation is described in ECM 1.10 • Wetlands may be mitigated. harm's way • Preserve function & character of riparian zones • Filter pollutants (esp. provide public open space area where Subchapter E doesn't apply) • Provide an ERM-approved restoration or enhancement plan for native vegetation/invasive plant management (IPM) plan with limited irrigation effective in undisturbed land in riparian soils) • Pervious pavers for sidewalks • Ensure infiltration volume is maintained (compensate on other areas of site for lost buffers) • Preserve trees and/or natural areas not already required to preserve • Apply Landscaping Ordinance for projects in the ETJ • Increase the CWQZ / WQTZ buffer to compensate or exceed for CWQZ / WQTZ encroachment • Preserve biologic and • Increased CEF buffer area from standard hydrogeologic integrity and the water quality/quantity for sensitive environmental resources requirement, and apply to unprotected areas that provide additional benefits to water quality/quantity • Exceed water quality requirements by providing enhanced stormwater treatment such as green infrastructure (e.g., raingardens, rain harvesting, constructed wetlands, enhanced infiltration/recharge) • Provide an ERM-approved restoration or enhancement plan for native vegetation/invasive plant management (IPM) plan with limited irrigation • Preserve trees and/or natural areas not already required to preserve (e.g., meet tree protection ordinance standards, including projects in the ETJ) • For caves, install an ERM-approved cave gate • For non-point recharge features, require a perimeter fence and gate occasional for driveway crossings or encroachments to allow "reasonable use", utility lines, reduction of floodplain area, redirect drainage ways. • Very few WQTZ variances requested (except in BSZ). • Subdivisions • Site Plans • Trams • Boat Docks • Driveways • Utility Lines • Drainage Modifications Env. Commission Variance mitigation table: EB Variances Page 2 of 4 COMMON VARIANCE REQUESTS & LOGICAL METHODS FOR THEIR EVALUATION Variance Request 5. Impervious • Net site area IC & density limits for all • Minimize runoff & Requirements Intent Mitigation Measures/Conditions Typical Examples Cover (IC) Density Net Site Area (NSA) wshed classifications except Urban • Urban wsheds use zoning IC limits only • IC allowed in WQTZ for Suburban wsheds (30%) and WS Suburban (18%) • Variances not allowed for SOS IC limits • Boundary street IC deductions in all but Urban wsheds (impact greatest in WS wsheds); IC deducted from site if road IC higher than site IC limit maximize infiltration to protect quality & quantity of surface & groundwater • Increase capacity/size and/or upgrade type of structural controls (esp. innovative Low Impact Development controls). [ECM 1.6.7] • Increased amount of impervious cover or density • Treat previously untreated off-site areas • Prohibit harmful land uses (e.g., service stations, • Boundary street impacts • Sites with little or no NSA • Limits established based auto repair, etc.) on sensitivity of watershed and impact on drinking water • Conserve open space • Increased creek setbacks • Pervious pavement for sidewalks • Clustered IC with undisturbed soils/vegetation • Increase the CWQZ / WQTZ buffer to compensate or 6. Placement of Fill in a Lake • Placement of fill in a lake is prohibited, unless necessary to restore an eroding shoreline as it existed 10 years prior to the date of the application • Prevent land capture, which converts CoA resources to private land • Preserve water volume of exceed for CWQZ / WQTZ encroachment • Preserve trees and/or natural areas not already required to preserve • Apply Landscaping Ordinance for projects in the ETJ • Infiltrate stormwater from impervious areas • Ensure no net loss of lake surface area through shoreline modifications elsewhere on the property where existing land becomes lake • Increase shoreline/riparian plantings by 25% over the reservoir what is ordinarily required • Preserve wetlands • Prevent ability of land • Bring existing non-compliant bulkheads to current code, with wave abatement and aquatic plantings owners to increase their land development rights through capture of land • If other options not possible, consider requiring payment into Riparian Zone Mitigation Fund 7. Dredging in Excess of 25 Cubic Yards From a Lake • Staff cannot administratively approve • Prevent sediment dredging in excess of 25 cubic yards discharge • Requires Section 404 of the Clean • Preserve shallow aquatic • Ensure that spoils disposal is effectively dealt with and that there is adequate construction access off site Water Act (CWA) Permit reviewed by U.S. Army Corps of Engineers vegetation • Mitigate potential damage to aquatic plants through • Prevent destabilization of additional wetland restoration lakebed • Limit amount of dredging for what is necessary for a standard size boat • Add fill to an existing cut- in slip • Previously unpermitted land capture under environmental enforcement action Dock cannot extend more than 30' from the shoreline, but existing shallow conditions prevent ability of a boat to enter a slip, or a boat lift to be installed within a slip Env. Commission Variance mitigation table: EB Variances Page 3 of 4 COMMON VARIANCE REQUESTS & LOGICAL METHODS FOR THEIR EVALUATION Requirements Intent Mitigation Measures/Conditions Typical Examples • Prevent excess • Ensure run-off from development is adequately development in buffer • Prevent erosion from destabilized banks • Preserve existing vegetation and ecosystem function of the riparian corridor controlled and that the proposed access won't cause additional erosion • Remove existing development from the lake CWQZ • Restore bank to excellent condition, as determined by functional assessment Applicant has existing stairs and wants to add a tram, ramp, etc. Variance Request 8. Shoreline Access Not Allowed in a CWQZ • For single family residences, necessary access is limited to the minimum area of disturbance necessary to construct a single means of access Appropriateness (Findings of Fact) Findings for Land Commission Variances: with approximately contemporaneous development; 2. The variance: 1. The requirement will deprive the applicant of a privilege or the safety of property given to owners of other similarly situated property a. b. is not based on a condition caused by the method chosen by the applicant to develop the property, unless the development method provides greater overall environmental protection than is achievable without the variance; is the minimum change necessary to avoid the deprivation of a privilege given to other property owners and to allow a reasonable use of the property; and c. does not create a significant probability of harmful environmental consequences; and 3. Development with the variance will result in water quality that is at least equal to the water quality achievable without the variance. Additional Findings for Stream Buffers: 4. The requirement for which a variance is requested prevents a reasonable, economic use of the entire property; and 5. The variance is the minimum change necessary to allow a reasonable, economic use of the entire property. GLOSSARY BSZ CEF CWQZ DDZ Dev’t ETJ IC IPM MFR NSA Barton Springs Zone Critical Environmental Feature Critical Water Quality Zone Desired Development Zone Development 5-mile Extra-Territorial Jurisdiction Impervious Cover Integrated Pest Management Multifamily Residential Net Site Area Multifamily Residential Net Site Area Right of Way Single Family Residence Save Our Springs Water Quality Water Quality Transition Zone Water Supply Rural MFR NSA ROW SFR SOS WQ WQTZ WS Rural WS Suburban Water Supply Suburban Wshed Watershed Env. Commission Variance mitigation table: EB Variances Page 4 of 4